Over the past few months, a new video about the dairy industry has been floating around the internet. Titled “Dairy is F*ing Scary”, it purports to show that dairy farming is cruel and inhumane. Erin Janus glibly rattles off dozens of myths about and misrepresentations of the dairy industry, while horrific images flash over the screen. I’ve watched the video numerous times, all the while shaking my head at the blatant lies gleefully rattling off this woman’s tongue. At the request of one of my blog readers, I’d like to try to address the claims Ms. Janus makes.
- Cows only lactate when they are pregnant or have given birth, so the dairy industry impregnates or inseminates dairy cows starting at the age of 12 months, over and over and over again so they keep making milk. Ms. Janus is right in that cows produce milk after giving birth, just like all mammals. When a heifer (female bovine that has not yet had her first calf) reaches sexual maturity (begins to ovulate) at around 6 months of age, she is not bred until she can safely carry a calf to term, typically at 15 months (not 12 months as Ms. Janus states). She is bred either by a bull or via artificial insemination. After giving birth nine months later at two years of age, she begins to produce milk to feed her calf. Dairy cattle have been selectively bred to produce greater quantities of milk than their beef-type cousins and often produce more milk than a calf can drink. On most dairy farms, calves are fed their mothers’ milk, and the excess is then shipped to the processor for human consumption. After this, cows are inseminated or bred once a year, but only if their health allows. This mimics the natural cycle of a cow giving birth once a year. In the wild, a cow is bred as soon as she comes into heat after giving birth to a calf, regardless of her health or her ability to carry a calf to term. On a dairy farm, only cows in good health are bred, and only after a few months have passed after she has given birth. If the cow is judged to be unfit for breeding, the farmer will wait until the cow is healthier and/or stronger and then breed her, typically at the advice of a veterinarian. A cow is milked until up to about two months before she is due to give birth again, then she goes on a sort of ‘maternity leave’, a time in which she is not milked, but spends her time eating, sleeping, and relaxing.
- Artificial Insemination: On some farms cows are bred by a bull. Other farmers prefer to use artificial insemination to impregnate their cows. They prefer this method so that they can match each individual cow to a bull that will produce a strong and healthy calf. For example, if the cow being bred has great conformation but does not produce a lot of milk, the farmer may choose to breed that cow with semen from a bull that has shown promising milk production in both his family and his progeny. Additionally, a bull on a farm can be dangerous, both to farmers and farm staff, but also to dairy cows. Artificial insemination can be gentler for a cow than being mounted by a 2000lb bull. Regardless of the method used, both have one purpose: impregnating a cow during her fertile period. So what does artificial insemination involve? Yes, semen is collected from bulls. However, this is not done on a dairy farm, but at specialized facilities that house these bulls for this purpose. And it’s not the sexually charged ordeal that Ms. Janus makes it out to be. Sex in animals does not involve emotion, but rather is a biological imperative to reproduce, not an act of love. The harvested semen then needs to be introduced to the cow’s reproductive tract. This is done via a small tube called a straw which is inserted into the cow’s vagina. Yes, a hand is also inserted into the cow’s anus, gently, and for the purpose of directing the semen straw to the cervix without damaging the cow’s reproductive tract. Again, this is NOT an act of bestiality, but rather of assisting a very natural process in a safe and gentle way.
- Calves are stolen from their mothers so that humans can drink the milk meant for the calf, and the mother cries for days in search of her baby. Calves are left with their mothers for a period of time after birth. This amount of time varies, and it depends on how well the mother cares for her calf. The truth is, many dairy cows don’t have much of a mothering instinct. Sad as it may sound, farmers can often do a better job taking care of a calf than a dairy cow can! I’ve seen cows neglect or ignore their calf, and we’ve even had some cows attack their calves! After some time has passed (usually between 24 and 48 hours on our farm) the calf is moved to the nursery where he/she is provided plenty of milk/colostrum from the mother cow; fresh, clean, soft bedding, and lots of love and attention from our family. Because of the high level of trust between us and the mother cow, which is generated by the level of care she has received her entire life on our farm, she does NOT cry for her calf, instead, she’ll usually continue eating or laying down when we move her calf. Sometimes we move the mother cow back to the herd before moving her calf to the nursery; in this scenario, once we open the gate the mother cow eagerly moves off to rejoin her herd-mates with nary a backwards glance at her calf. Neither does the calf cry for her mother, she’s perfectly content in her new surroundings. On our farm, and on all of the many farms I’ve visited, calves are fed their mother’s first milk via bottle and then milk from the herd by pail or nipple bucket as they grow older. As I have stated above, a dairy cow can produce much more milk than her calf can drink. Farmers take absolute care to make sure that the calves drink enough colostrum in the first hours after they are born. This can be difficult to judge if a calf is nursing, which is why most farm will supplement with extra bottle-fed colostrum even if the calf is nursing from the mother. This colostrum is fed within a few hours after birth to make sure the calf gets enough of this high calorie wonder food that is full of essential antibodies – the ability to absorb colostrum declines after a few hours. (Colostrum is never shipped to the processor, if a cow has too much for her calf, it is frozen to feed to other calves whose mothers may not have sufficient amounts for their own calf.) After the first few days, calves are given whole milk from the herd as opposed to colostrum. Most farms wean the calves from milk around 2-3 months of age, onto a diet of hay, grains and other forages as their digestive systems mature. But what about the horrific clips shown of cows chasing after their calves that are being dragged away by a cruel farmer or cows bellowing loudly? Unfortunately, just like in all walks of life, the dairy industry does have some bad apples. These clips are awful examples of bad cow management practices. However, this does not mean that things like this happen on all farms. Abuse does happen; it is not the norm, but the very rare exception. On all of the farms I’ve visited, separation of cows and calves is done in a calm, quiet, and gentle manner in order to make the transition as relaxed as possible. We’re not in the business of causing unnecessary trauma to the animals on our farms, but rather we do whatever we can to keep our cows happy and comfortable. Cows will bellow for many reasons, including for food, in unfamiliar situations, and when they are in heat (their fertile period). Without showing the context of why these cows are vocalizing in these video clips, Ms. Janus lets the viewer assume that these cows are crying for their babies, while this very probably is not the case!
- Dairy cows are continuously kept pregnant their whole lives to keep them lactating. This leads to premature aging, exhaustion, and mastitis. See point #1 regarding cows being ‘kept pregnant’. As I stated there, it is natural for a cow to give birth once and year, and this would happen without a farmer’s intervention if a cow had access to a bull. Giving birth yearly does not lead to premature aging, exhaustion, or mastitis. Just like humans, cows also can get mastitis, which is an infection of the udder. It is not caused by giving birth every year, but is caused by bacteria entering the udder. It can be avoided by ensuring that barns and milking equipment are clean and sterile. This infection is treated with antibiotics. While a cow is being treated with antibiotics and until the drug-specific milk withdrawal time has passed, her milk is discarded. For an in-depth look at what the milking process involves, see this previous post, here.

Bright and airy barns, and sparkling clean milking equipment help minimize the chance of our cows getting udder infections.
- Bull (male) male calves are all killed as veal. Ms. Janus states that all bull (male) calves have their throats slit and are sold as veal, implying that this happens right after birth. Our male (bull) calves remain on our farm for a few weeks, and then another farmer takes over raising them for beef. The bull calves are raised on a completely balanced diet of forages and grains and then are slaughtered for beef once they reach an appropriate weight, usually near 2 years of age. There are some veal farms in Canada, but the majority of bull calves are raised as beef, not veal. Additionally, many veal farms in Canada no longer use veal crates for raising veal, but have renovated or retrofitted their barns to allow for group housing with plenty of room for the veal calves to roam around. These new standards of care, outlawing veal crates, will be mandatory in a few years. Veal are slaughtered at 4 to 6 months, not as tiny baby calves.

This 2 week old bull calf is treated just like his female counterparts – plenty of food, water, clean bedding. He’s treated with respect and compassion.
- Pus and blood in milk. I’ve written an entire blog post on this myth. Find it here. A short summary: There is NO pus or blood in milk. Canadian farmers like myself, as well as all farmers around the world, must comply with very strict standards regarding the components and purity of milk. Milk that does not meet these standards is not shipped to the processor and the farmer must correct his procedures in order to resume shipping milk. The myth of pus in milk arises from the equating of somatic cells with pus. Ms. Janus says it’s the “same stuff that erupts from the top of a big zit”. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Pus is made up of dead white blood cells, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Somatic cells are living white blood cells located in the udder of cows. Like all white blood cells, they fight infection. An elevated somatic cell count indicates that the cow is fighting some sort of infection. Milk is tested both on farm and at the processing plant; one of the tests run is called a “somatic cell count” test. This test shows the level of somatic cells in a sample of milk. A herd with an average somatic cell count of 200 000 cells per milliliter is generally considered to be in optimum health, there are likely very likely few if any cows in that herd with poor udder health. The maximum allowable limit for somatic cells in milk is 400 000. This line is drawn to ensure that sick cows are treated and that their milk does not enter the food chain. Additionally, herd somatic cell counts under 250 000 receive a monthly monetary bonus; in our province about 80% of the herds often receive this bonus. This proves that the milk you buy in the grocery stores comes from healthy cows.
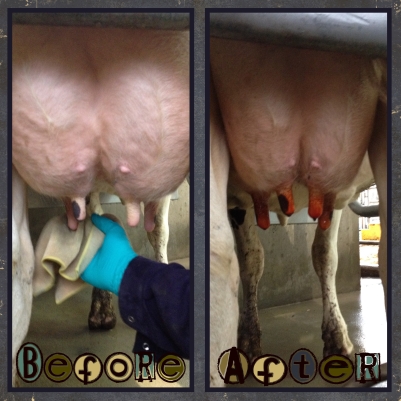
A healthy udder on a healthy cow. No swelling, hard quarters or redness to indicate mastitis. In the “after” photo, the teats have been coated with an iodine based substance to minimize the chances of bacteria entering the teat canal.
- “Downers”. Sometimes cows become sick. When they do, farmers use every tool they have to help their cow regain her health, often with the help of a veterinarian. Occasionally, a cow will be too ill to stand. These cows are sometimes called “downers”. A downed cow is not killed and sold for beef…EVER. The Canadian Code of Practice for the Care and Handling of Dairy Cattle contains strict regulations on how to handle downed cows. They are NOT treated in the abusive way that is shown in the undercover videos. This type of treatment would result in criminal prosecution. Downed cows are moved in the gentlest way possible to a comfortable hospital pen. In Canada, only a cow that can walk onto a transport truck can be shipped to slaughter. It is illegal to ship a downed cow, and so these cows are either nursed back to health or humanely euthanized on farm. Cows don’t “go down” after four or five years of milk production. Neither does their milk production decline at 4-5 years of age. On the contrary, their milk production is usually still increasing at that stage of their lives! On our farm, and on many farms that I have visited, cows will often stay on the farm for much longer, sometimes well into their teens. But at the end of those 8-10 (average on our farm) years, they don’t all “go down”. Instead, they are shipped to slaughter as healthy animals in order to supply our Canadian consumers with beef.
- Milk and Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis Canada, Canada’s national osteoporosis research and education organization, recommends “3 servings of milk and alternatives (2 servings for adults under age 50) – yogurt, cheese, calcium-fortified beverages, puddings, custards, etc. This essentially means that, if you are over 50, you need the equivalent of one good serving of dairy at each meal” to help prevent osteoporosis. I’d think that an organization like this would be more informed about reducing the risks of osteoporosis than an internet quack, no? And I think Health Canada along with the actual doctors and nutritionists that recommend that dairy products be included in the Canadian Food Guide know more about a healthy diet than an activist. (Of course, there certainly are other sources of dietary calcium, it’s definitely not only found in milk, and it’s definitely possible to get enough calcium from a diet that does not include dairy products.)
- Abuse on dairy farms. Abuse to dairy cows, and to any animal, is never, ever ok. The clips Ms Janus shares deeply saddened me; I can’t understand how anyone could treat an animal in the manner shown in this video. Along with our fellow Canadian dairy farmers, we are committed to continuously improving animal welfare. We strive to do this through funding animal care research, attending educational sessions, investing in technology to improve the life of the animals, as well as with supporting the proAction Initiative for a sustainable future. Animal health and welfare is a top priority for Canadian farmers who work with veterinarians and nutritionists to provide the best conditions for cows. Unfortunately, as can be seen in this awful video, some individuals treat animals poorly and inhumanely. This is reprehensible, disgusting, and devastating to us as dairy farmers, and to the whole industry. Dairy Farmers of Canada and all provincial dairy farmer organizations are working to continually advocate for enforcements against abuse and Canadian dairy farmers are very transparent about how they care for their animals, which can be seen by our efforts to show the public our farms and informing them in other ways about common dairy practices. All farmers are expected to adhere to the Code of Practice and treat their animals with respect and compassion. Our industry promotes on-farm training and materials for farmers to educate their employees on the importance of providing proper care for animals treating them with dignity and respect. The Animal Care Code of Practice clearly emphasizes the importance of good animal care and reporting any incidence of animal abuse immediately. Abuse is definitely not the norm, there is no motive or reason for a farmer to abuse his/her cows: even if a farmer cared nothing for the cows under their care, every farmer knows that happy, comfortable, healthy, well cared for cows produce the best quality milk, and no farmer wants to jeopardize their income or bottom line. But beyond this, as farmers we treat our cows well because it simply is the right thing to do. Period.
************************
For real information about how cows are treated on family farms like ours, I’d like to invite you to take a peek at our Facebook page.
You can find it in the left hand margin of this blog.
********************
I have nothing against those who choose not to include dairy products in their diet. However, I hope that your choice was not based on biased propaganda similar to what is shown in this video. Additionally, I will not stand idly by when my integrity and the integrity of my fellow dairy farmers is attacked. Portraying dairy farmers as abusive and sexually sadistic not only is patently false, but it verges on slander. I’m trying to do my part to slow the spreading of lies about the way cows are treated on dairy farms and the misrepresentation of common dairy practices. I’m not a corporate spokesman or a crazed activist. I’m just a hard-working farmer, and I’m not getting paid a dime to write any of this. I wanted to write this article for the sole purpose of promoting the truth and correcting the false information that I’ve seen all over my social media feeds. I hope that after reading this (rather lengthy – sorry!) article, you’ll now feel assured that dairy farmers go about their daily work with one purpose: caring for their animals with respect and compassion while providing a safe and nutritious product for consumers.
add: this link has a ton of resources comparing milk to other non-dairy beverages: https://milklife.com/milk-vs-non-dairy-milk-alternatives/



















